IPGrabber, a term encompassing various techniques for stealing IP addresses, presents a significant cybersecurity threat. This exploration delves into the methods used to acquire IP addresses, the risks associated with such theft, and the protective measures individuals and organizations can employ. We will examine both the technical mechanisms behind IP grabbers and the broader ethical and legal implications of their use, providing a comprehensive understanding of this evolving threat landscape.
From simple scripts to sophisticated malware, IP grabbers utilize diverse methods to obtain an individual’s or organization’s IP address. Understanding these methods, from phishing campaigns to exploiting software vulnerabilities, is crucial for effective mitigation. This analysis will detail the various attack vectors, the consequences of a successful attack, and strategies for prevention and response.
Understanding IP Grabbers
IP grabbers are tools used to obtain the IP addresses of internet users. Understanding how they work, their malicious uses, and protective measures is crucial for online safety.
IP Grabber Definition and Types
An IP grabber is a piece of software or script designed to secretly collect the IP addresses of internet users. These addresses identify a device’s location on a network. IP grabbers can range from simple scripts to sophisticated malware. Different types exist, categorized by their methods of operation and target.
IP Grabber Creation and Deployment Methods
IP grabbers are typically created using programming languages like Python or JavaScript. They often leverage vulnerabilities in web applications or operating systems to collect IP addresses. Deployment methods include embedding them in malicious websites, distributing them through phishing emails, or packaging them within malware.
Malicious Uses of IP Grabbers
IP grabbers are frequently used for malicious purposes, including targeted attacks, tracking user activity, and facilitating further cybercrimes. For example, an attacker might use an IP grabber to identify the location of a target before launching a more serious attack like DDoS or spear phishing.
Comparison of IP Grabber Techniques
The following table compares different IP grabber techniques, their effectiveness, and the difficulty in detecting and mitigating them.
Obtain access to pokemon r34 to private resources that are additional.
| Technique | Description | Detection Difficulty | Common Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| JavaScript Injection | Malicious JavaScript code embedded in websites to capture IP addresses. | Moderate | Regular security audits, web application firewalls (WAFs). |
| Malicious Email Attachments | IP grabbers distributed via infected email attachments. | Low (if detected) | Email security solutions, employee training on phishing awareness. |
| Drive-by Downloads | IP grabbers downloaded automatically when visiting compromised websites. | High | Up-to-date antivirus software, safe browsing habits. |
| Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities | IP grabbers leveraging vulnerabilities in software to gain access and collect IP addresses. | High | Regular software updates and patching. |
How IP Grabbers Function

Understanding the technical mechanisms behind IP grabbers is key to effective prevention and response. This section details the process of IP address acquisition and data transmission.
Technical Mechanisms of IP Grabbers
IP grabbers primarily exploit the inherent functionality of network protocols. They leverage HTTP headers, which contain the client’s IP address, to obtain this information. Some more sophisticated methods might involve analyzing network traffic or exploiting vulnerabilities in applications to access this data directly.
Methods of Obtaining a Victim’s IP Address
An IP grabber obtains a victim’s IP address by various means. Common methods include parsing HTTP headers, analyzing network packets, or utilizing compromised systems to collect IP address information from the network.
Vectors for Delivering IP Grabbers
IP grabbers are often delivered through various vectors. Phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links are a common method. Malware infections can also install IP grabbers onto compromised systems. Drive-by downloads, where malicious code is automatically downloaded when visiting a compromised website, are another vector.
Process of Sending Stolen Data
Once an IP address is collected, the grabber typically sends it to a remote server controlled by the attacker. This is often done using standard network protocols like HTTP or HTTPS, making detection challenging. Data might be encrypted to avoid interception.
Common Vulnerabilities Exploited
Several common vulnerabilities are frequently exploited by IP grabbers.
- Unpatched software vulnerabilities
- Weak or default passwords
- Lack of network security measures
- Phishing susceptibility
- Out-of-date operating systems
Risks and Consequences of IP Grabber Attacks
The theft of IP addresses can lead to significant risks for individuals and organizations. This section explores these risks and provides real-world examples.
Potential Risks of IP Address Theft
Stolen IP addresses can be used for various malicious activities, including targeted attacks, network intrusion, identity theft, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. The attacker can use the IP address to pinpoint the victim’s location and potentially launch further attacks.
Real-World Examples of Malicious Use
Numerous instances demonstrate the malicious use of IP grabbers. For example, botnets often use IP grabbers to identify vulnerable systems for further exploitation. In some cases, IP grabbers have been used to track journalists and activists, compromising their safety and privacy.
Legal Implications
Creating and using IP grabbers for malicious purposes is illegal in most jurisdictions. Penalties can range from fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the crime and the intent of the attacker.
Potential Damage to Individuals and Organizations
The damage caused by IP grabber attacks can be significant. Individuals may experience identity theft, privacy violations, and financial losses. Organizations may face data breaches, reputational damage, and financial losses.
Flowchart of an IP Grabber Attack
A typical IP grabber attack follows these steps:
1. Initial Infection (e.g., phishing email, malicious website).
2. IP Grabber Installation.
3.
IP Address Collection.
4. Data Transmission to Attacker’s Server.
5. Further Exploitation (e.g., DDoS attack, data breach).
Protecting Against IP Grabbers
Implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect against IP grabber attacks. This section details preventative measures for individuals and organizations.
Preventative Measures
Several preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of IP grabber attacks.
- Keep software updated.
- Use strong, unique passwords.
- Practice safe browsing habits.
- Implement firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Use anti-malware software.
Importance of Network Security Practices, Ipgrabber
Strong network security practices are paramount. This includes regularly updating firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security software.
Role of Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems play a crucial role in preventing and detecting IP grabber attacks by monitoring network traffic and blocking suspicious activity.
Use of VPNs
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) encrypt internet traffic and mask the user’s IP address, making it more difficult for IP grabbers to collect information.
Best Practices for Prevention
The following table Artikels best practices for preventing IP grabber attacks.
| Practice | Description | Implementation Difficulty | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Software Updates | Keeping software patched to address known vulnerabilities. | Low | High |
| Strong Passwords | Using complex and unique passwords for all online accounts. | Low | High |
| Firewall Implementation | Installing and configuring a firewall to control network traffic. | Moderate | High |
| Antivirus Software | Using reputable antivirus software to detect and remove malware. | Low | High |
Detection and Response to IP Grabber Attacks
Early detection and a well-defined incident response plan are critical for minimizing the impact of an IP grabber attack.
Signs of an IP Grabber Infection
Signs of an IP grabber infection may include unusual network activity, slow performance, and unexpected pop-ups or error messages. Monitoring network traffic for suspicious outbound connections is crucial.
Methods for Detecting Malicious Network Activity
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and network monitoring tools can help detect malicious network activity, such as unusual connections to unknown servers.
Analyzing Network Traffic
Analyzing network traffic logs can reveal suspicious connections or data exfiltration attempts. Tools like packet sniffers can be used to examine network traffic in detail.
Removing an IP Grabber
Removing an IP grabber requires immediate action. This involves running a full system scan with updated antivirus software, isolating the affected system from the network, and potentially reinstalling the operating system.
Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan is crucial. The steps involved include:
- Identify and contain the affected systems.
- Analyze the extent of the compromise.
- Remove the IP grabber.
- Restore affected systems.
- Strengthen security measures.
- Monitor for further activity.
Ethical Considerations
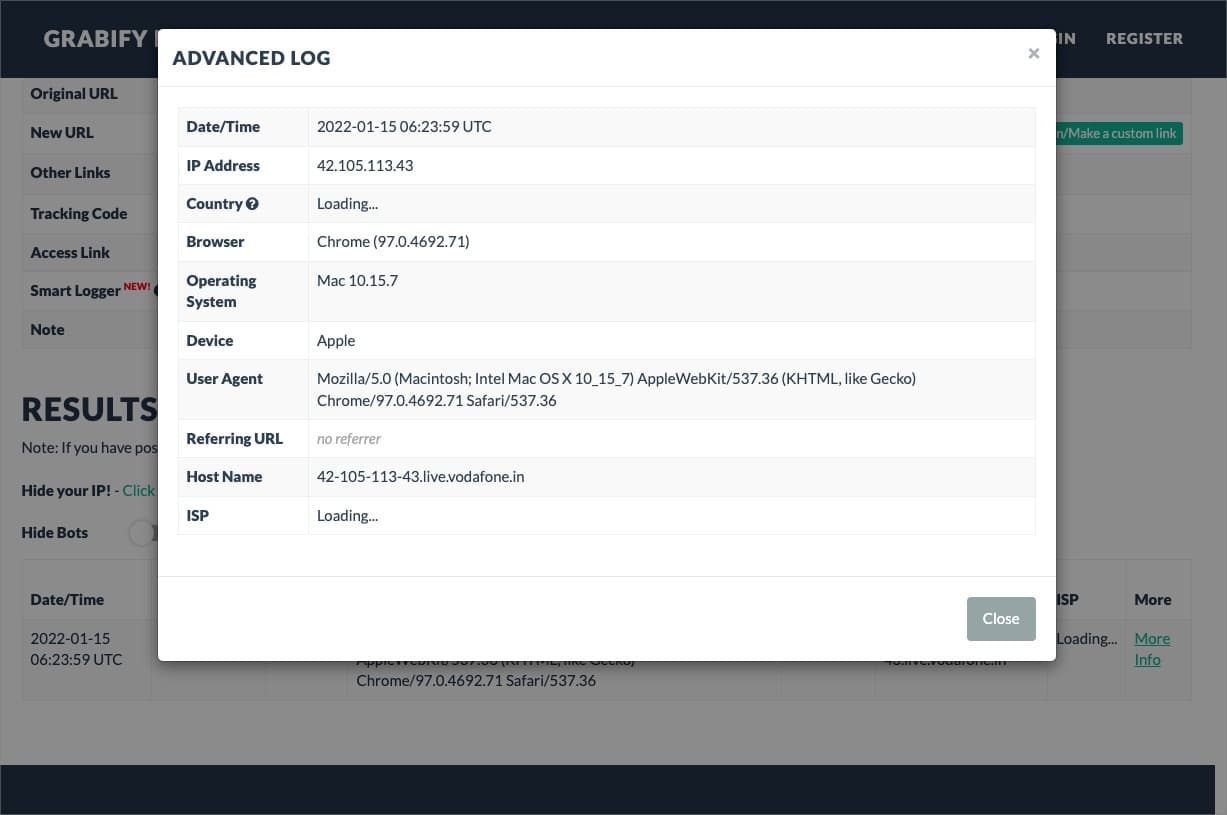
The development and use of IP grabbers raise important ethical considerations, particularly in the context of security research and ethical hacking.
Ethical Implications in Security Research
Developing IP grabbers for security research requires careful consideration of ethical implications. Researchers should obtain proper authorization before testing vulnerabilities and always adhere to responsible disclosure practices.
Ethical Hacking vs. Malicious Activities
The distinction between ethical hacking and malicious activities is crucial. Ethical hackers use IP grabbers (with permission) to identify vulnerabilities and improve security, while malicious actors use them for illegal purposes.
Responsible Disclosure Practices
Responsible disclosure involves reporting vulnerabilities to the affected party privately, allowing them to address the issue before public disclosure.
Adherence to Legal and Ethical Guidelines
Adhering to legal and ethical guidelines is paramount. This includes obtaining informed consent, respecting privacy, and avoiding any actions that could cause harm.
Ethical Considerations for Security Professionals
Security professionals working with IP grabbers should always prioritize ethical considerations.
- Obtain proper authorization before using IP grabbers.
- Respect privacy and confidentiality.
- Adhere to responsible disclosure practices.
- Avoid any actions that could cause harm.
- Comply with all applicable laws and regulations.
In conclusion, IP grabbers pose a substantial threat, demanding a proactive and multi-layered approach to security. While the techniques used are constantly evolving, a strong understanding of the underlying mechanisms, coupled with robust preventative measures and a well-defined incident response plan, are crucial for mitigating the risks associated with IP address theft. Staying informed about emerging threats and best practices remains paramount in the ongoing battle against cybercrime.
Questions and Answers: Ipgrabber
What is the difference between an IP grabber and a keylogger?
An IP grabber specifically targets IP addresses, while a keylogger captures keystrokes. They are distinct types of malware with different objectives.
Can an IP grabber be used for legitimate purposes?
While IP grabbers can be used in ethical hacking for security assessments (with proper authorization), their use for malicious purposes is far more prevalent and illegal.
How can I detect if my IP address has been compromised?
Unusual network activity, unexpected login attempts, and changes in your network settings are potential indicators. Regular security scans can also help detect malicious software.
What is the legal penalty for creating or using an IP grabber?
Penalties vary by jurisdiction but can include significant fines and imprisonment, depending on the severity and intent of the crime.



